Clinical gait analysis is a vital part of podiatry and can offer transformative solutions for individuals struggling with pain, injury, or discomfort. It involves a detailed study of the movement of the feet, ankles, knees, and hips to pinpoint any issues with biomechanics.
In most cases, a podiatrist will observe your gait by watching you walk in the quiet hallway of their clinic or on a treadmill. However, more advanced techniques are available for a more complete assessment.
Biomechanics
Having powerful feet and joints that function as they should is essential to moving effectively and gracefully. However, faulty foot mechanics can easily lead to abnormalities in the way you move which can cause pain and injury.
In standard gait analysis, podiatrists like the experts from Doubleview Podiatry Perth will observe your body movement while you walk around or run on a treadmill. In a computerised gait analysis, high-tech cameras and sensors build a digital image of your body’s movements allowing for a more detailed evaluation of the dynamic function of your feet and how your bones and muscles work together.
Using advanced pressure mapping technology, an Innaloo podiatrist can assess how force is distributed through the feet and identify areas of excessive pressure that may be contributing to your symptoms. This information is useful when designing or modifying orthotic devices, shoes and shoe modifications. In addition, it helps to determine if there is a leg length discrepancy (LLD) that cannot be detected through observation or palpation. It also provides important information regarding the first ray function and how propulsion is generated.
Pronation
Pronation is the foot and ankle’s natural action when a person walks or runs. During this process, the arch of your foot rolls inward to distribute weight evenly across the foot and reduce impact stress. However, when excessive pronation occurs, it can cause the arch to collapse. This causes the foot to roll downward and inward even further, with the weight getting transferred to the outside of the foot and small toes. This can lead to shin splints, heel spurs and bunions.
The most obvious sign of overpronation is a dropped arch. It can be assessed with static postural assessment and a visual inspection of the feet. Alternatively, weight bearing (or non-weight bearing) X-rays can be taken to confirm overpronation.
While everyone pronates, too much pronation can cause problems. You can help alleviate this by wearing shoes designed for your arch type and using foot exercises to strengthen the arch and ankle. Investing in custom orthotics can also be helpful for people who suffer from excess pronation. In addition, palpatory examination is important to assess the foot muscles for tightness and myofascial trigger points.
Posture
Many of us are constantly told to ‘sit up straight’ or ‘don’t slouch’. While it is true that our posture is important, the way we hold our body while we are moving is also crucial. Posture is how we keep our body stable while moving and is controlled by a combination of muscles, ligaments and joints.
We need to have the right amount of strength, flexibility and balance in our posture. This is what allows our muscles to work efficiently and prevents muscle fatigue. It also helps to prevent joint, cartilage and ligament damage.
If our posture is not correct, it can lead to poor alignment, and this in turn can cause a whole host of problems in other areas of the body including back pain, neck or shoulder pain, pinched nerves, low stamina and fatigue, headaches, breathing difficulties, sprains, and muscle injuries.
Traditional views of good posture insist on the idea that there is one ‘correct’ way to stand, sit and lie. However, it is now widely believed that it may be more helpful to encourage postural variability and cultivate the ability to adjust your posture to different situations.
Heel strike
There is little that divides the running community more than opinions about foot strikes. Some believe that heel strike running is bad for knees, while others swear by it as the best way to run. Regardless of your opinion, it is important to understand what impact load your feet are taking when you run and how this can affect injury risk.
Heel strike runs are associated with greater shock load in the knees and heels, which may lead to common conditions such as Sever’s Disease (calcaneal apophysitis). Midfoot and forefoot runners, on the other hand, absorb most of the impact load within their ankles. This can lead to less strain on the Achilles tendon and lower leg muscles, which may reduce the risk of injury.
The problem is that the change in load to the ankle and calf muscle complex can also result in an increased amount of load through the knee joint. A recent study found that a runner’s body is forced to use more hip and knee movement when switching from heel strike to forefoot strike, which is not as efficient from an energy perspective.
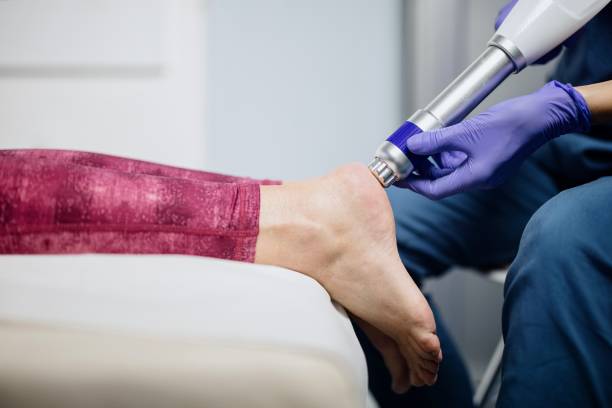
Pressure mapping
Pressure mapping is a clinical tool that measures interface pressure between the body and surface. It enables you to identify areas of high stress, which can be a source of skin damage. It can be used by physiotherapists, occupational therapists and orthotists to redistribute skin-damaging pressure and prevent pressure ulcers.
A pressure map consists of a mat with sensors that measure the distribution of pressure, producing a color-coded image on a computer screen with numerical data. The image is arranged so that it resembles a topographical contour map and shows the locations of peak pressures. Often, these areas are formed over bony prominences.
To record a pressure map, the participant remains in their usual sitting position for 8 min to adapt to the device. Then the device records their pressure distribution for 2 min. The results are then displayed and analysed on the software. The correlations between the pressure mapping variables and functional tests were numerous, especially in the multiple sclerosis group. It suggests that these neurological pathologies behave in a unique way and therefore require specific treatment approaches.
In summary, the utilisation of gait analysis done in a local podiatry clinic is pivotal in diagnosing and treating various foot and lower limb conditions. Through meticulous observation and advanced technologies like computerised gait analysis and pressure mapping, podiatrists can gain profound insights into biomechanical abnormalities, pronation issues, posture discrepancies, and foot strike patterns. These insights not only aid in understanding the root causes of pain and discomfort but also inform personalised treatment plans, which may include orthotic devices, footwear modifications, strengthening exercises, and postural adjustments. By integrating these analytical tools into clinical practice, podiatrists can offer comprehensive care aimed at optimising foot function, alleviating symptoms, and improving overall mobility and quality of life for their patients.